Skin Diseases Treatment
Your skin is the largest organ in your body and is constantly exposed to the elements.
As a result, it is vulnerable to a wide range of diseases and conditions.
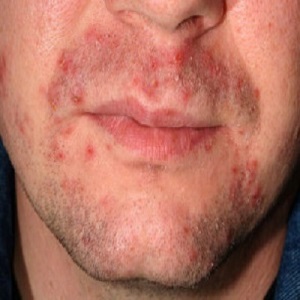
The good news is that many skin diseases can be treated effectively with the right care and treatment.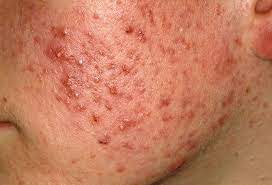 Acne commonly manifests as pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads, and can be accompanied by inflammation and redness.
Hormonal changes, excess oil production, bacteria, and clogged pores contribute to its development.
Treatment approaches range from over-the-counter products containing salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide to prescription medications, such as antibiotics or retinoids.
It's important to consult a dermatologist for personalized recommendations and to adopt a consistent skincare routine for managing acne effectively.
Acne commonly manifests as pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads, and can be accompanied by inflammation and redness.
Hormonal changes, excess oil production, bacteria, and clogged pores contribute to its development.
Treatment approaches range from over-the-counter products containing salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide to prescription medications, such as antibiotics or retinoids.
It's important to consult a dermatologist for personalized recommendations and to adopt a consistent skincare routine for managing acne effectively.
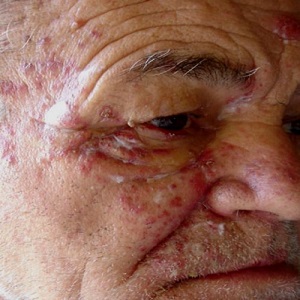
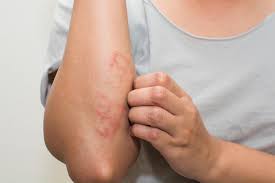 Eczema also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and red patches on the skin.
It often appears in childhood but can persist into adulthood. Triggers can include irritants, allergens, stress, and changes in temperature or humidity.
Treatment typically involves a combination of moisturizers, topical corticosteroids, and avoidance of triggers.
In severe cases, oral medications or phototherapy may be prescribed.
It's important to work with a dermatologist to develop an individualized treatment plan for managing eczema symptoms effectively.
Eczema also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and red patches on the skin.
It often appears in childhood but can persist into adulthood. Triggers can include irritants, allergens, stress, and changes in temperature or humidity.
Treatment typically involves a combination of moisturizers, topical corticosteroids, and avoidance of triggers.
In severe cases, oral medications or phototherapy may be prescribed.
It's important to work with a dermatologist to develop an individualized treatment plan for managing eczema symptoms effectively.
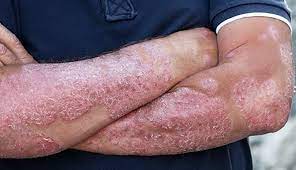 Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin, causing the rapid buildup of skin cells.
This leads to the formation of thick, red patches covered with silvery scales. The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is believed to be
influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Treatment options include topical medications, systemic medications, light therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
Proper management can help control symptoms and improve quality of life for individuals with this condition.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin, causing the rapid buildup of skin cells.
This leads to the formation of thick, red patches covered with silvery scales. The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is believed to be
influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Treatment options include topical medications, systemic medications, light therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
Proper management can help control symptoms and improve quality of life for individuals with this condition.
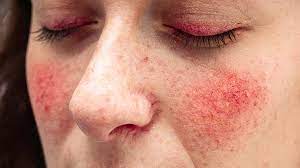 Rosacea is a common chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, flushing, visible blood vessels,
and in some cases, small red bumps or pustules. It tends to affect fair-skinned individuals and can worsen with triggers like sunlight, heat, spicy foods, and alcohol.
While the exact cause of rosacea is unknown, factors such as genetics, immune system dysfunction, and abnormal blood vessel response may contribute to its development.
Treatment options include topical medications, oral antibiotics, laser therapy, and lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Consulting with a dermatologist is essential for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Rosacea is a common chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, flushing, visible blood vessels,
and in some cases, small red bumps or pustules. It tends to affect fair-skinned individuals and can worsen with triggers like sunlight, heat, spicy foods, and alcohol.
While the exact cause of rosacea is unknown, factors such as genetics, immune system dysfunction, and abnormal blood vessel response may contribute to its development.
Treatment options include topical medications, oral antibiotics, laser therapy, and lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Consulting with a dermatologist is essential for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
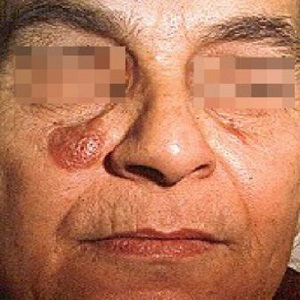
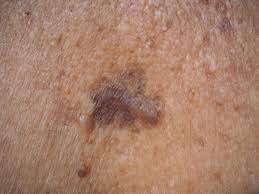 Skin cancer is the abnormal growth of skin cells, primarily caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds.
The most common types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
Early detection and treatment are crucial for successful outcomes. Regular self-examinations and professional skin checks are recommended to identify any suspicious
moles, lesions, or changes in the skin. Sun protection measures, such as wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and seeking shade, are vital in preventing skin cancer.
If diagnosed, treatment options may include surgical removal, radiation therapy, or targeted drug therapy, depending on the type and stage of cancer.
Skin cancer is the abnormal growth of skin cells, primarily caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds.
The most common types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
Early detection and treatment are crucial for successful outcomes. Regular self-examinations and professional skin checks are recommended to identify any suspicious
moles, lesions, or changes in the skin. Sun protection measures, such as wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and seeking shade, are vital in preventing skin cancer.
If diagnosed, treatment options may include surgical removal, radiation therapy, or targeted drug therapy, depending on the type and stage of cancer.
These include:
The good news is that many skin diseases can be treated effectively with the right care and treatment.
Common Skin Diseases
 Acne commonly manifests as pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads, and can be accompanied by inflammation and redness.
Hormonal changes, excess oil production, bacteria, and clogged pores contribute to its development.
Treatment approaches range from over-the-counter products containing salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide to prescription medications, such as antibiotics or retinoids.
It's important to consult a dermatologist for personalized recommendations and to adopt a consistent skincare routine for managing acne effectively.
Acne commonly manifests as pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads, and can be accompanied by inflammation and redness.
Hormonal changes, excess oil production, bacteria, and clogged pores contribute to its development.
Treatment approaches range from over-the-counter products containing salicylic acid or benzoyl peroxide to prescription medications, such as antibiotics or retinoids.
It's important to consult a dermatologist for personalized recommendations and to adopt a consistent skincare routine for managing acne effectively.
 Eczema also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and red patches on the skin.
It often appears in childhood but can persist into adulthood. Triggers can include irritants, allergens, stress, and changes in temperature or humidity.
Treatment typically involves a combination of moisturizers, topical corticosteroids, and avoidance of triggers.
In severe cases, oral medications or phototherapy may be prescribed.
It's important to work with a dermatologist to develop an individualized treatment plan for managing eczema symptoms effectively.
Eczema also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that causes dry, itchy, and red patches on the skin.
It often appears in childhood but can persist into adulthood. Triggers can include irritants, allergens, stress, and changes in temperature or humidity.
Treatment typically involves a combination of moisturizers, topical corticosteroids, and avoidance of triggers.
In severe cases, oral medications or phototherapy may be prescribed.
It's important to work with a dermatologist to develop an individualized treatment plan for managing eczema symptoms effectively.
 Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin, causing the rapid buildup of skin cells.
This leads to the formation of thick, red patches covered with silvery scales. The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is believed to be
influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Treatment options include topical medications, systemic medications, light therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
Proper management can help control symptoms and improve quality of life for individuals with this condition.
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the skin, causing the rapid buildup of skin cells.
This leads to the formation of thick, red patches covered with silvery scales. The exact cause of psoriasis is unknown, but it is believed to be
influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Treatment options include topical medications, systemic medications, light therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
Proper management can help control symptoms and improve quality of life for individuals with this condition.
 Rosacea is a common chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, flushing, visible blood vessels,
and in some cases, small red bumps or pustules. It tends to affect fair-skinned individuals and can worsen with triggers like sunlight, heat, spicy foods, and alcohol.
While the exact cause of rosacea is unknown, factors such as genetics, immune system dysfunction, and abnormal blood vessel response may contribute to its development.
Treatment options include topical medications, oral antibiotics, laser therapy, and lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Consulting with a dermatologist is essential for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
Rosacea is a common chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, flushing, visible blood vessels,
and in some cases, small red bumps or pustules. It tends to affect fair-skinned individuals and can worsen with triggers like sunlight, heat, spicy foods, and alcohol.
While the exact cause of rosacea is unknown, factors such as genetics, immune system dysfunction, and abnormal blood vessel response may contribute to its development.
Treatment options include topical medications, oral antibiotics, laser therapy, and lifestyle modifications to manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Consulting with a dermatologist is essential for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
 Skin cancer is the abnormal growth of skin cells, primarily caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds.
The most common types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
Early detection and treatment are crucial for successful outcomes. Regular self-examinations and professional skin checks are recommended to identify any suspicious
moles, lesions, or changes in the skin. Sun protection measures, such as wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and seeking shade, are vital in preventing skin cancer.
If diagnosed, treatment options may include surgical removal, radiation therapy, or targeted drug therapy, depending on the type and stage of cancer.
Skin cancer is the abnormal growth of skin cells, primarily caused by prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds.
The most common types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
Early detection and treatment are crucial for successful outcomes. Regular self-examinations and professional skin checks are recommended to identify any suspicious
moles, lesions, or changes in the skin. Sun protection measures, such as wearing sunscreen, protective clothing, and seeking shade, are vital in preventing skin cancer.
If diagnosed, treatment options may include surgical removal, radiation therapy, or targeted drug therapy, depending on the type and stage of cancer.
Treatment Options
- Topical medications: Creams, gels, and ointments applied directly to the skin to reduce inflammation and clear up blemishes.
- Oral medications : Pills and capsules taken by mouth to reduce inflammation and improve the overall condition of the skin.
- Light therapy : Exposure to UV or visible light to slow down the production of skin cells and reduce inflammation.
- Cryotherapy : Freezing the affected skin cells to destroy them and promote healing.
- Surgery : Removal of skin cancer cells with surgical procedure
- Chemical Peels : Use of chemical solution to remove the damaged outer layers of the skin to reveal a new, smoother and clearer skin.
Prevention
While some skin diseases cannot be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of developing certain conditions.These include:
- Protecting your skin from the sun by using sunscreen and wearing protective clothing.
- Keeping your skin moisturized to prevent dryness and itching.
- Not picking or squeezing blemishes to prevent infection and scarring.
- Avoiding smoking and drinking alcohol
- Eating a balanced diet, including fruits, vegetables and lean protein
- Avoiding stress
- Exercising regularly
To know more about the Treatment of Skin Diseases Kindly contact : Dr Amey Kelkar
 |
 |
 |