Psoriasis Treatment
Get expert Psoriasis Treatment at Derma Solutions! Say goodbye to itching, redness, and discomfort with advanced dermatology care. Safe, effective, and personalized solutions for healthy skin. Book your appointment today!

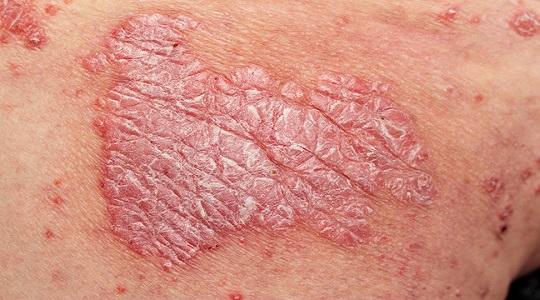
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that primarily affects the skin, causing red, scaly, and often itchy patches. It occurs when the immune system triggers an accelerated skin cell production process, leading to the buildup of dead skin cells on the surface. While psoriasis can vary in severity, it often disrupts daily life and can have a significant emotional impact on those affected. Fortunately, there are various treatment options available to help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life.
Types of Psoriasis
Psoriasis manifests in several forms, each with distinct characteristics. The main types include:
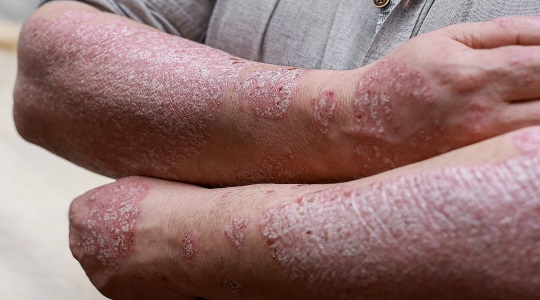
Plaque Psoriasis (Psoriasis Vulgaris)
- The most common type, characterized by raised, red patches covered with a silvery-white buildup of dead skin cells.
- Commonly appears on the scalp, elbows, knees, and lower back.
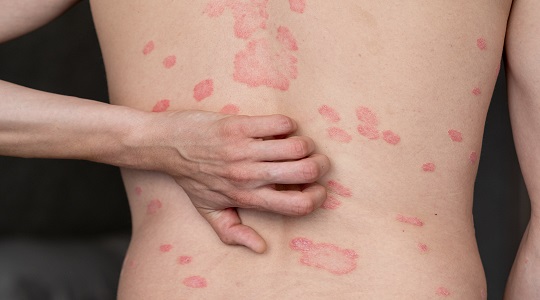
Guttate Psoriasis
- Appears as small, drop-shaped sores on the skin.
- Often triggered by infections like strep throat.
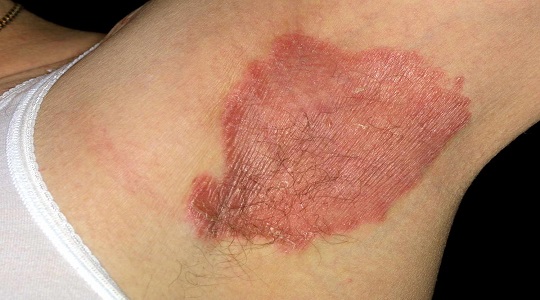
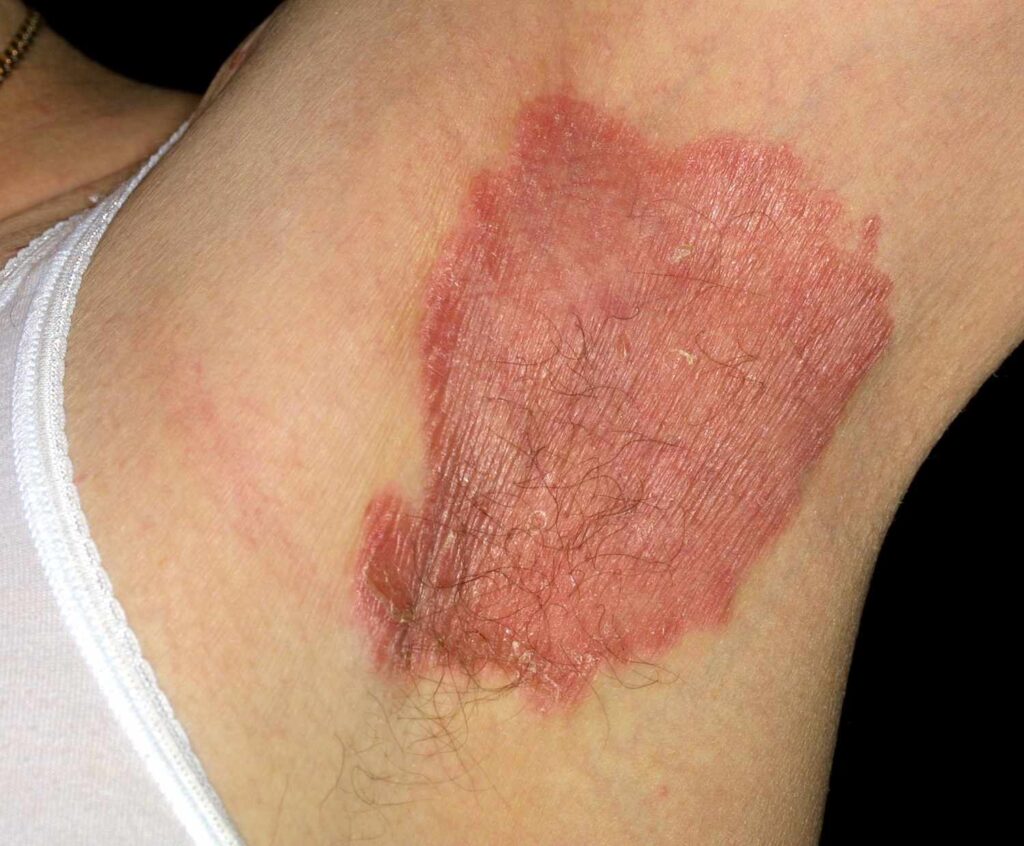
Inverse Psoriasis
- Occurs in skin folds, such as under the breasts, around the groin, or near the buttocks.
- The affected areas appear shiny and red.
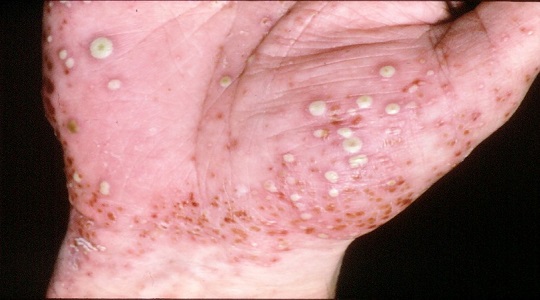
Pustular Psoriasis
- Characterized by white pustules (blisters filled with pus) surrounded by inflamed skin.
- Can appear on localized areas, such as the hands and feet, or across the entire body.
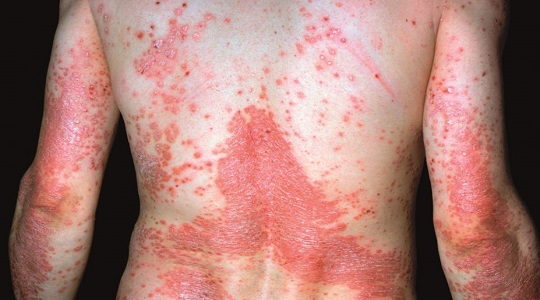
Erythrodermic Psoriasis
- A severe form that causes widespread redness, shedding, and intense itching or pain.
- Requires immediate medical attention.
Who is at the risk of developing a Psoriasis ?
Psoriasis can affect anyone, but certain factors may increase the risk:

Genetics Predisposition: Having a family history of psoriasis significantly increases the likelihood of developing the condition.

Age: Although psoriasis can develop at any age, it most commonly appears between the ages of 15 and 35.

Stress Levels: High levels of stress can trigger or exacerbate psoriasis

Infections: Bacterial or viral infections, such as strep throat or HIV, can act as triggers.

Lifestyle Factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and obesity can increase the risk and severity of psoriasis.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
Symptoms can vary depending on the type of psoriasis and its severity. Common symptoms include:
- Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales.
- Dry, cracked skin that may bleed.
- Itching, burning, or soreness in affected areas.
- Thickened or ridged nails (psoriatic nails).
- Joint pain or stiffness in cases of psoriatic arthritis.
Causes of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is primarily an autoimmune disorder. While the exact cause remains unclear, it involves a complex interplay of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors. Key causes include:
- Immune System Dysfunction:
- An overactive immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to rapid cell turnover and buildup.
- Genetic Factors:
- Certain genetic markers are associated with an increased risk of psoriasis.
- Environmental Triggers:
- Triggers such as infections, injuries, stress, or weather changes can initiate or worsen psoriasis.
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Smoking, heavy alcohol use, and poor diet may exacerbate the condition.
Psoriasis Treatment and Management
Managing symptoms, reducing inflammation, and slowing down skin cell production. Treatment depends on the type, severity, and location of psoriasis.
Topical and Supportuve Care: Dermatologists may suggest topical approaches to help calm inflammation, reduce scaling, and support skin health. Regular moisturization plays an important role in maintaining the skin barrier.
Advanced Care Options:
In some cases, supervised light-based therapies or other advanced medical options may be considered by a specialist based on individual needs.Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies:
- Healthy Diet: Include anti-inflammatory foods.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques.
- Skincare Routine: Use gentle, fragrance-free products.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and avoid factors that worsen symptoms.
Prevention and Management of Psoriasis
While psoriasis cannot be cured, proactive management can help minimize flare-ups:
- Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and avoid smoking or excessive alcohol.
- Protect Your Skin: Avoid skin injuries, harsh soaps, and prolonged sun exposure
- Stay Hydrated: Keep your skin moisturized to prevent dryness and irritation.
- Manage Stress: Reduce stress levels to prevent triggers.
- Regular Medical Check-Ups: Work closely with a dermatologist to monitor and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
Book your experience
Our expert team is ready to help you achieve radiant, healthy skin with Psoriasis treatment tailored just for you.
Enhance your beauty
Reveal your natural glow with expert beauty treatments designed to enhance your confidence.

Book an appointment

Get your schedule

Meet with our expert





