Hair Fall Treatment
Hair loss can be caused by various factors, including genetics (male and female pattern baldness), hormonal changes (such as pregnancy, menopause, or thyroid issues), stress, poor diet, medical conditions (like alopecia or scalp infections), and certain medications. Lifestyle factors and environmental damage can also contribute to Hair Fall or Hair Loss.


Many people including Men and Women are affected by Hair loss.
It can occur on the scalp, eyebrows, beard, and other parts of the body.
Hair loss can be caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, hormonal changes, medical conditions, and stress.
Some of the most common symptoms of hair loss include thinning hair, bald patches, and excessive shedding.
In more severe cases, hair loss can lead to complete baldness or significant reduction in hair density.
Some of the most common symptoms of hair loss include thinning hair, bald patches, and excessive shedding.
In more severe cases, hair loss can lead to complete baldness or significant reduction in hair density. Hair Fall and Masturbation – Is There Really a Link?
Types of Hair Loss
There are different types of Alopecia Areata, each with its own set of symptoms and patterns of hair loss. The severity and extent of hair loss can vary from person to person. Below are the main types of this condition:

Androgenetic Alopecia (Male and Female Pattern Baldness)
Androgenetic alopecia, also known as pattern baldness, is a common form of hair loss that primarily affects the scalp. Symptoms include gradual thinning of hair on the crown and temples in men, while women may experience overall thinning without a receding hairline. In some cases, complete baldness may develop in men. Fortunately, androgenetic alopecia can often be managed with treatments like minoxidil, finasteride, and hair transplantation. It’s important to follow a prescribed treatment plan and maintain scalp health to slow down progression.
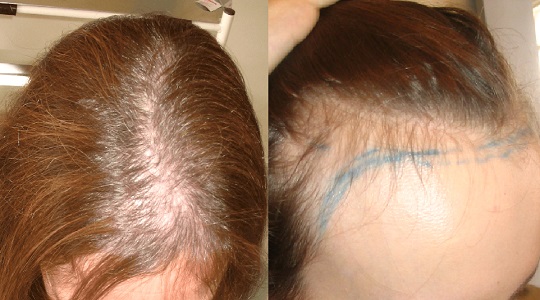
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition that leads to sudden hair loss in small, round patches on the scalp or other body parts. This condition occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, causing them to shrink. Alopecia areata is unpredictable and can progress to total scalp hair loss (alopecia totalis) or complete body hair loss (alopecia universalis). Treatment typically involves corticosteroids, immunotherapy, or minoxidil to encourage hair regrowth.

Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a temporary form of hair loss caused by stress, illness, surgery, or hormonal changes. It leads to excessive shedding of hair, particularly after a triggering event such as childbirth, severe illness, or emotional distress. The condition is characterized by hair thinning rather than bald patches. Telogen effluvium often resolves on its own once the underlying cause is addressed, but proper nutrition and hair supplements may support regrowth.

Traction Alopecia
Traction alopecia is a type of hair loss caused by constant pulling or tension on the hair. It commonly occurs due to tight hairstyles like ponytails, braids, and hair extensions. Symptoms include hair breakage, thinning along the hairline, and in severe cases, permanent hair loss if the pulling continues over time. Treatment involves avoiding tight hairstyles, using gentle hair care techniques, and in some cases, applying topical treatments to stimulate hair regrowth
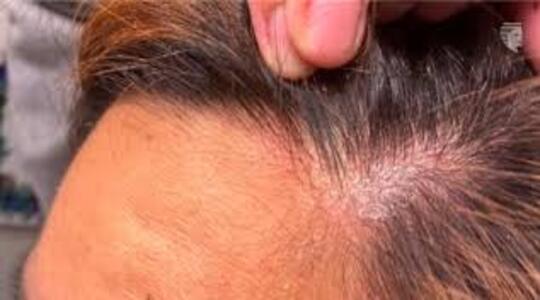
Scalp Infections and Hair Loss
Certain fungal or bacterial infections, such as tinea capitis (scalp ringworm), can cause hair loss by affecting hair follicles. Symptoms may include itchy, red patches, flaking, or scaly skin on the scalp. Infections can lead to temporary hair loss, which usually resolves with appropriate treatment. Antifungal or antibacterial medications are commonly prescribed to eliminate infections and promote hair regrowth.
Who is at Risk of Developing Hair Loss?
You may have a higher risk for developing hair loss if you:

Have a family history of hair loss.

Experience severe physical or emotional stress

Have underlying medical conditions such as thyroid disorders, anemia, or autoimmune diseases.

Have nutritional deficiencies, especially low iron and protein levels.

Take certain medications like chemotherapy drugs, beta-blockers, or antidepressants.

Undergo hormonal changes due to pregnancy, menopause, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).

Frequently wear tight hairstyles or hair accessories.

Hair Loss Treatment and Symptoms
- Topical treatments, such as minoxidil, which is applied directly to the scalp.
- Oral medications, which helps block the hormone responsible for hair loss.
- Hair transplant surgery, which involves moving hair follicles from one area to another.
Symptoms of Hair Loss
Hair loss can occur gradually or suddenly, depending on the underlying cause. Here are the most common symptoms:
- Thinning Hair – Gradual hair thinning before complete loss in some cases.
- Brittle or Weak Nails – Nail changes like ridges, pitting, or brittleness.
- Thinning Hair – Gradual hair thinning before complete loss in some cases.
- Tingling or Itching – Some individuals experience mild tingling or itching in affected areas.
- Color Change in Hair – Regrown hair may have a different color or texture.

Causes of Hair Loss
- Genetics (Androgenic Alopecia) – Inherited hair loss causing thinning, receding hairline, or bald spots.
- Hormonal Imbalances – DHT in men and hormonal changes in women (pregnancy, menopause, PCOS) trigger hair loss.
- Thyroid Disorders – Hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and autoimmune diseases (Hashimoto’s, Graves’) cause thinning.
- Stress & Trauma – Emotional or physical stress can lead to excessive shedding (telogen effluvium).
- Nutrient Deficiencies – Lack of iron, vitamin D, biotin, or protein weakens hair follicles.
Book your experience
Our expert team is ready to help you achieve radiant, healthy skin with treatments tailored just for you.
Enhance your beauty
Reveal your natural glow with expert beauty treatments designed to enhance your confidence.

Book an appointment

Get your schedule

Meet with our expert





